Variable Valve Timing Solenoid: Testing and Inspection
OIL CONTROL VALVE (OCV) INSPECTION [L3 WITH TC]Unable to Keep Idling
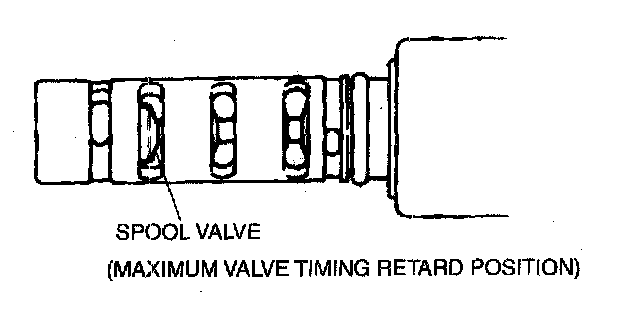
1. Remove the OCV.
2. Verify that the spool valve inside the OCV is at the maximum valve timing retard position as shown in the figure.
- If there is any malfunction, replace the OCV.
3. Connect the OCV connector.
4. Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
5. Verify that the spool valve inside the OCV is at the maximum valve timing retard position.
- If there is any malfunction, inspect the harnesses and connectors between the OCV and PCM for a short circuit.
6. Inspect the variable valve timing actuator.
Able to Keep Idling
When using the SST (WDS or equivalent).
1. Connect the SST (WDS or equivalent).
2. Warm up the engine.
3. Using the VT DUTY1 simulation function, set the duty value of the OCV to 100% and verify that the engine idles roughly or stalls.
- If it idles roughly or stalls, verify the timing chain assembly (valve timing).
- If it does not idle roughly or stall, perform the following inspection.
1) Remove the OCV and connect the OCV connector.
2) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
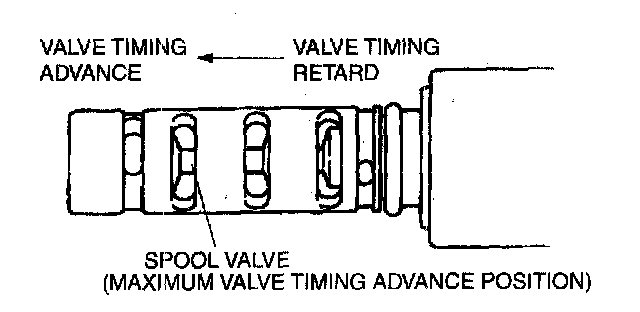
3) Using the VT DUTY1 simulation function, change the duty value for the OCV from 0% to 100%, and then verify that the spool valve inside the OCV operates and moves to the maximum valve timing advance position.
- If it does not operate, inspect OCV operation and the wiring harnesses and connectors between the OCV and PCM for a short circuit or disconnection.
4) Inspect the hydraulic passage for leakage.
Hydraulic passage
Between the oil pressure switch and the OCV
Between the OCV and the camshaft
Oil passage inside the camshaft
5) If the inspected parts are normal, replace the variable valve timing actuator.
When not using the SST (WDS or equivalent)
1. Disconnect the OCV connector.
2. Start the engine and idle it.
3. When applying battery positive voltage between the oil control valve terminals, verify if the engine rough idles or stalls.
- If it idles roughly or stalls, verify the timing chain assembly (valve timing).
- If it does not idle roughly or stall, perform the following inspection.
Note:
- When applying battery positive voltage between the oil control valve terminals, the connection of the positive and negative cables can be either terminal A or B.
1) Inspect OCV operation.
2) Inspect the harnesses and connectors between the OCV and PCM for a disconnection and short circuit.
3) Inspect the hydraulic passage for leakage.
Hydraulic passage
Between the oil pressure, switch and the OCV
Between the OCV and the camshaft
Oil passage inside the camshaft
4) If the inspected parts are normal, replace the variable valve timing actuator.
Coil Resistance Inspection
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the OCV connector.
3. Measure the coil resistance between terminals A and B using a tester.
- If it is not within the specification, replace the 0CV.
Oil control valve resistance 6.9 - 7.9 ohms [20°C (68°F)]
4. Connect the OCV connector.
Spool Valve Operation Inspection

1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove the OCV.
3. Verify that the spool valve inside the OCV is at the maximum valve timing retard position as shown in the figure.
- If there is any malfunction, replace the OCV.
4. Verify that the battery is completely charged.
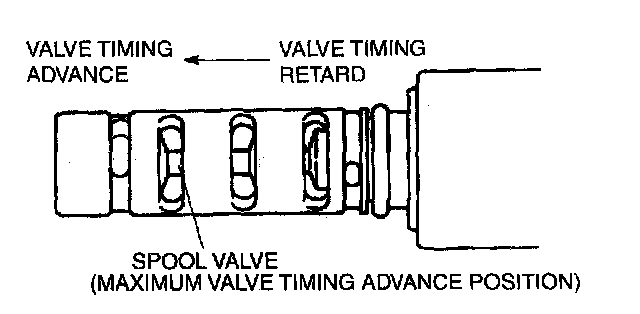
5. When battery positive voltage is applied between 0(',V terminals A and B, verify that the spool valve moves to the maximum valve timing retard position.
- If there is any malfunction, replace the 0CV.
Note:
- When applying battery positive voltage between the OCV terminals, the connection of the positive and negative cables can be either terminal A or B.
6. Stop applying battery positive voltage and verify that the spool valve returns to the maximum valve timing advance position.
- If there is any malfunction, replace the OCV.
7. Install the OCV.